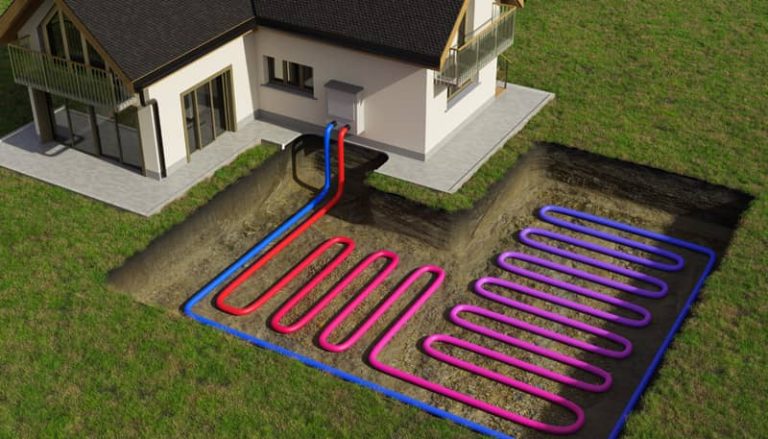
For heating renovations
To change the heating system in an existing house, it is important to take into account the current installations. If you already have ventilation ducts for a forced air heating system, installing a heat pump could be the simplest and least expensive choice…
Additional costs
Apart from the cost of the system, it is important to consider installation costs, usage costs, maintenance costs, etc.
It is noteworthy to mention that electricity rates are more expensive in Ontario than In Quebec. But the consumption level in Quebec is higher mainly because of the colder climate and the wider use of electricity than gas for heating.
SEER Rating
SEER stands for seasonal energy efficiency ratio. It is an energy efficiency measure that evaluates the energy consumed against the energy released by the device. The higher the SEER, the more efficient the device and the less energy it consumes.